Diversity of life:
How many different types of living organisms are there?
There are about 1.5 million known species and about 10 million estimated. Yes, we have discovered only a fraction of the living creatures out there.
To make sense of that many living things we cluster them.
This is Carolus Linnaeus--the father of taxonomy (the field of classifying and naming organisms):

Using his system we subdivide all living things into broad categories called Kingdoms
Then Phylum
Then Class
Then Order
Then Family
Then Genus
Then Species
And sometimes Subspecies
Of course we usually just call them by their genus and species (i.e. Homo Sapian) rather than their full name (i.e. Animalia Chordata Mammalia Primates Hominidae Homo Sapian - this would translate roughly to "animal, backbone, mammal, primate, human, wise man")
The kingdoms have changed over the years (Linnaeus said there were two--plantae and animalia), but right now most taxonomists say their are 6. They are:
Archeabacteria
Eubacteria
Protista
Fungi
Plantae
Animalae
Get ready for a trip through the biodiversity on Earth...
This is to give you an appreciation for the wondrous diversity and complexity out there; you are not meant to memorize millions of organisms. So, sit back and enjoy:

These guys are tiny, simple, found in strange places, and not much to look at.
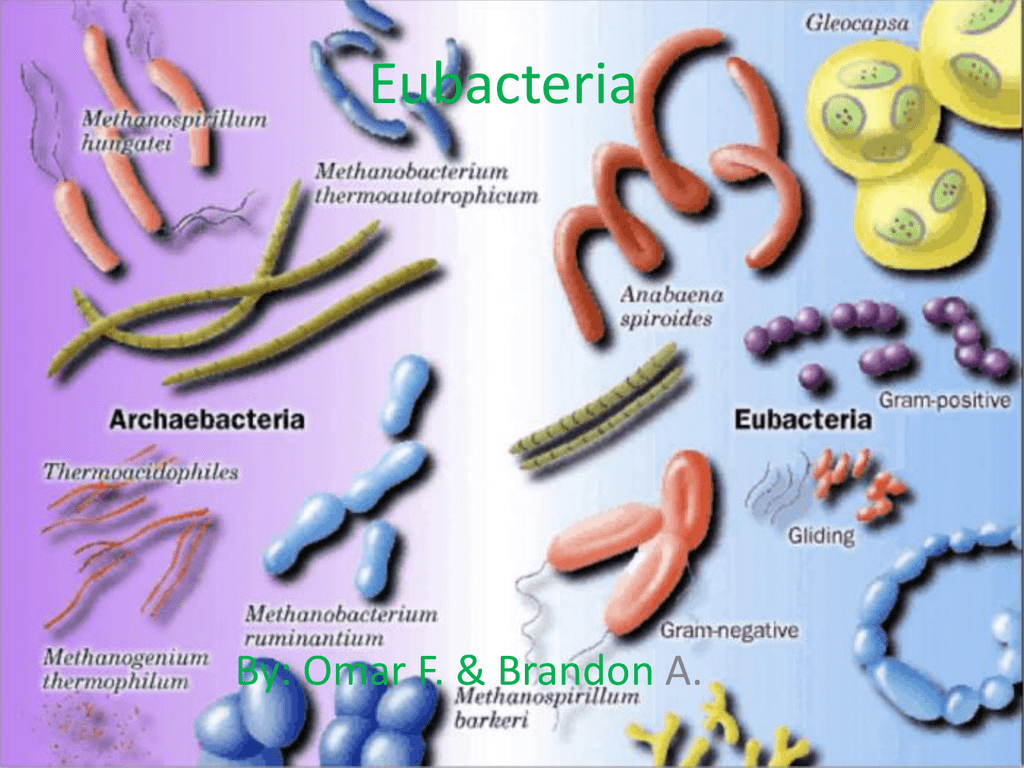
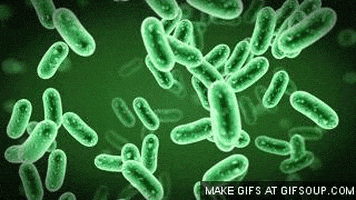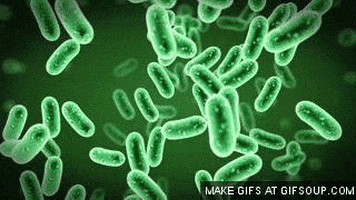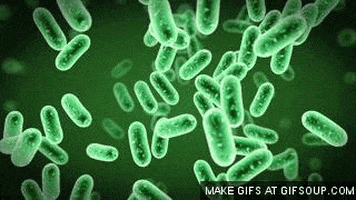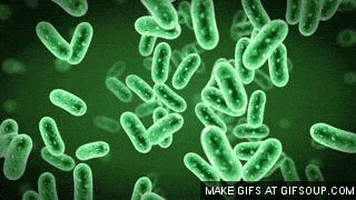
Eubacteria are also tiny and simple and not much to look at, but they are found absolutely everywhere! There are more bacteria in you than there are your own cells in you and you don't exist without them. No life does. We need the nitrogen fixing and decomposing abilities of these little guys.
Neither archeabacteria, nor eubacteria have much inside their cells but DNA. They are super simple and extremely small. They used to be called non-filterable, because we had no screen small enough to catch them.
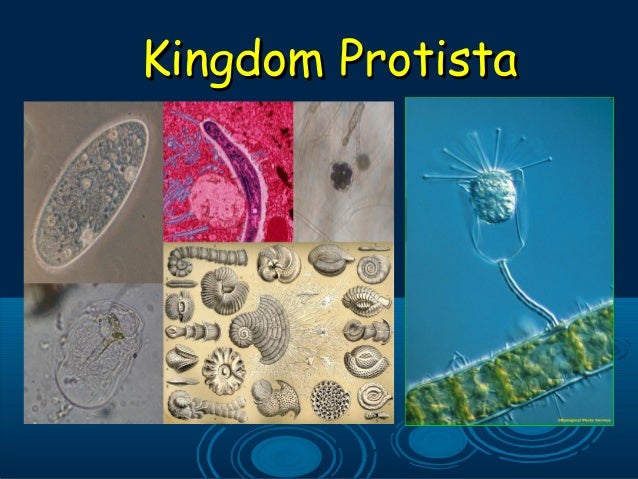
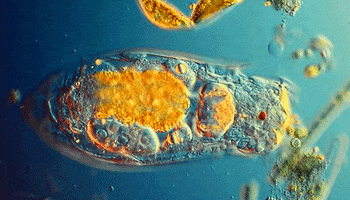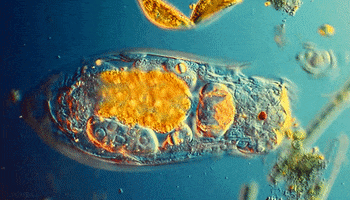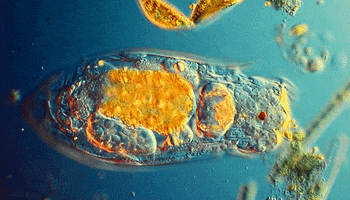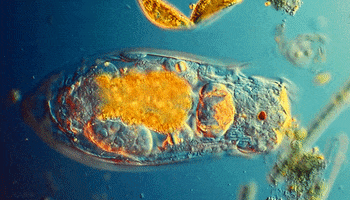

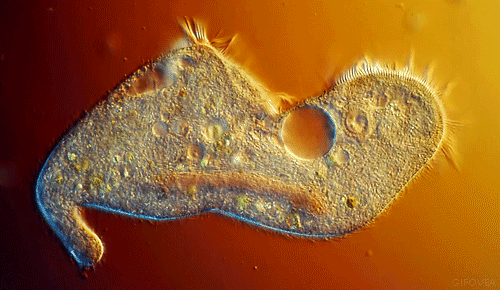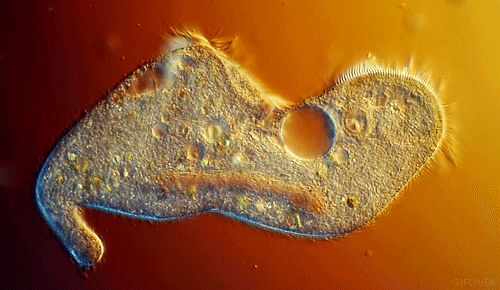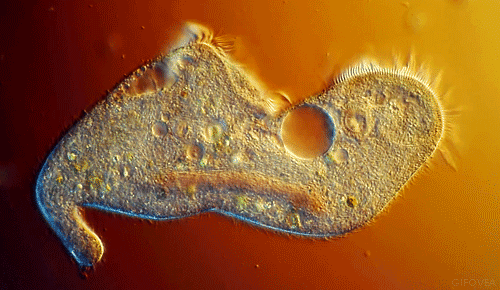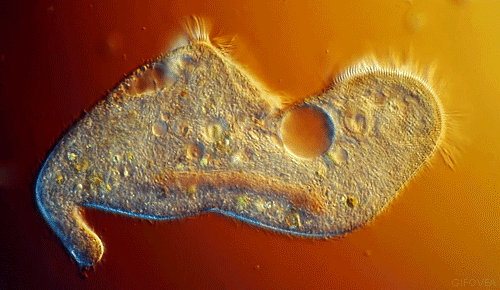
These little guys are also single-celled, but they start to get interesting. They move and look cool. They have flagella, cilia, or psuedopods to allow them to locomote. They move about the world and eat things and used to be called tiny animals. Their cells have little tiny organs in them called organelles (as do the more complex organisms).




You can actually see these guys. They used to be grouped in with plants, but they are heterotrophs (they eat other things). Included here are yeasts, jellies, molds, smuts, and mushrooms. They make our cheese and alcohol.
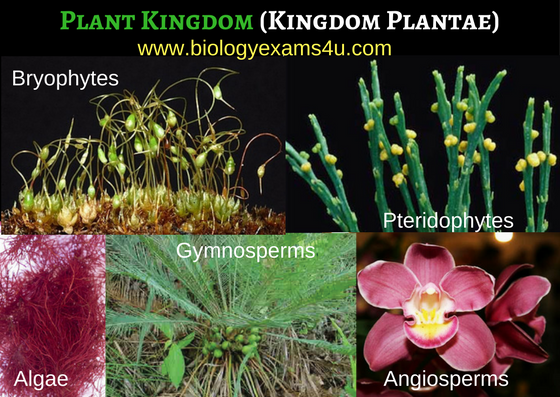

The simple ones have no way to transport nutrients or support themselves. The more complex ones make flowers and grow very tall. They can live thousands of years and have tremendous and wondrous variety.
The animals will be subdivided by order from simple to complex:

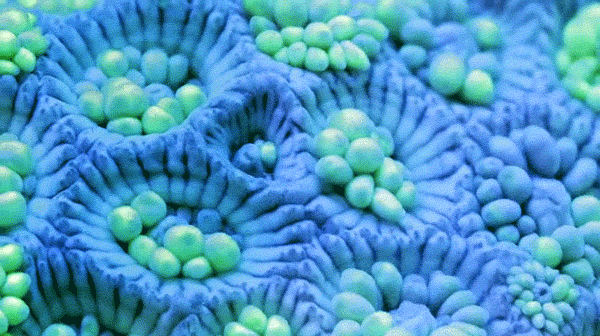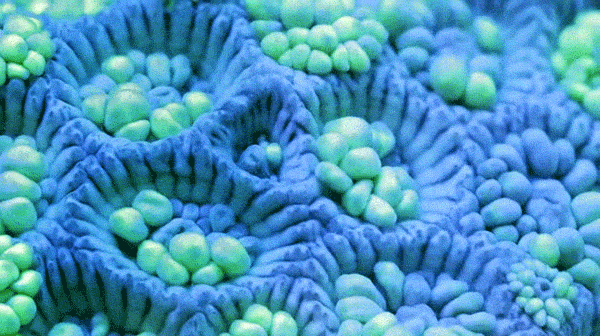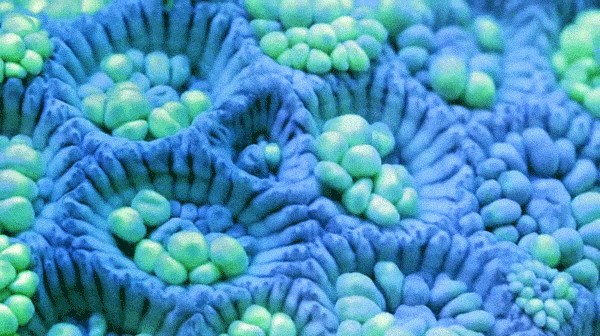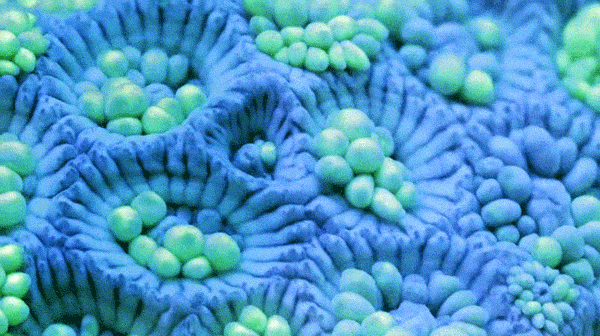
Sponges

Cnidaria include jellyfish and sea anemoes.

Flatworms and roundworms.

Starting to get more complex, huh?

Octopuses, clams, snails, etc. are mollusks
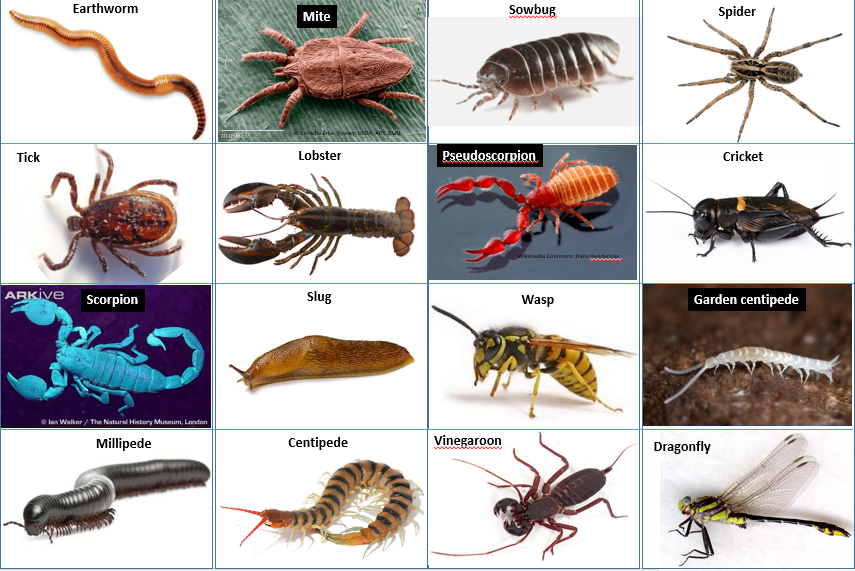

Arthropods include insects, spiders, lobsters, and just about anything like that with an exoskeleton. This is the most diverse and plentiful of all animal orders. But, despite the image above, earthworms and slugs are not arthropods.
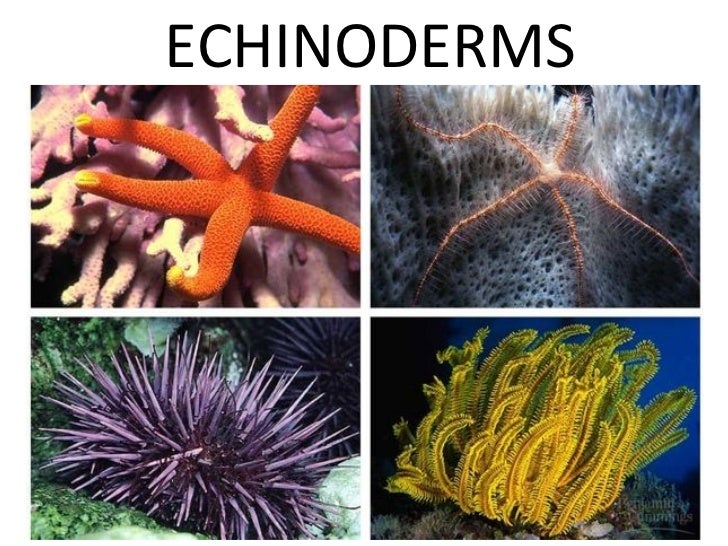

Starfish and sea urchins.

Lamprey are an order all their own. There parasites bite onto other fish and suck their blood as they hitch a ride.
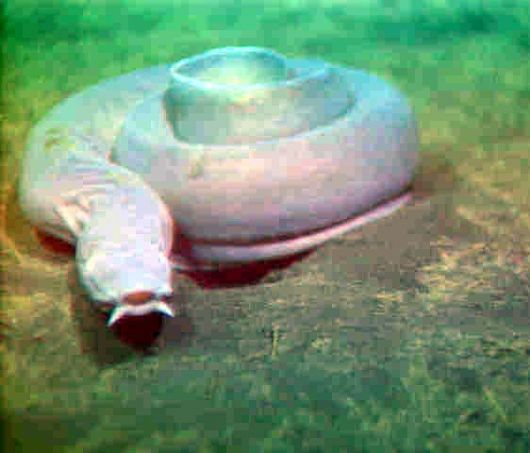

Hagfish also get their own order. They have funny mouths and produce thick slime.

Sharks and rays and skates make up this order of boneless fishes.

Then there are bony fishes. They have bones.
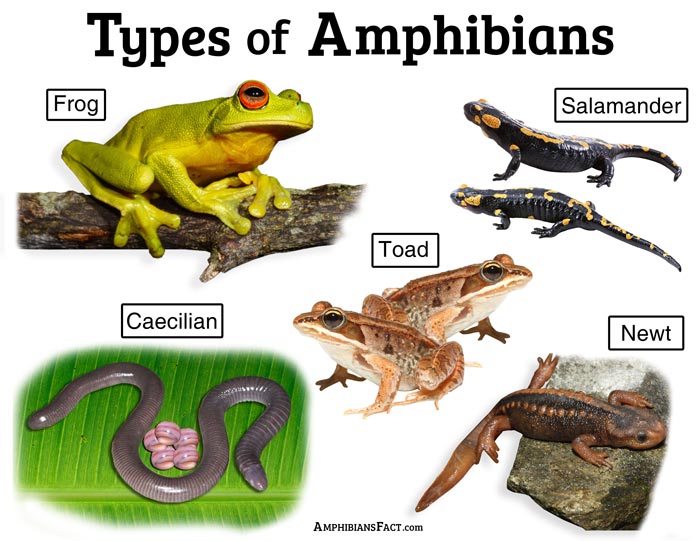
These guys need water to reproduce. Many are wetland creatures, but some (like toads) can thrive in the desert.

Reptiles are scaly cousins to the amphibians.

Birds have four chambered hearts and feathers. Some swim, some walk, some fly, they are diverse.

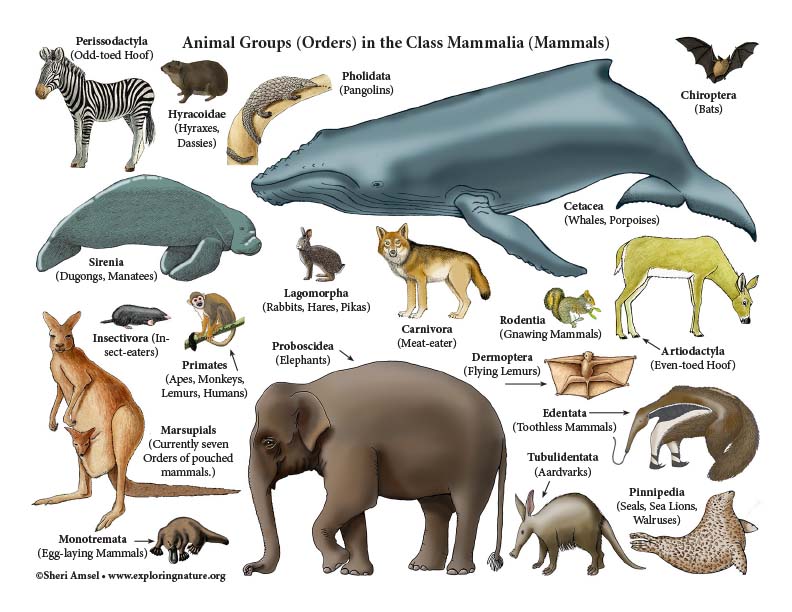
Mammals include humans, whales, dogs, bats, platypuses, etc. They all make milk for their young. Most have fur. Most give birth to live young.
Is that it?
What about viruses?
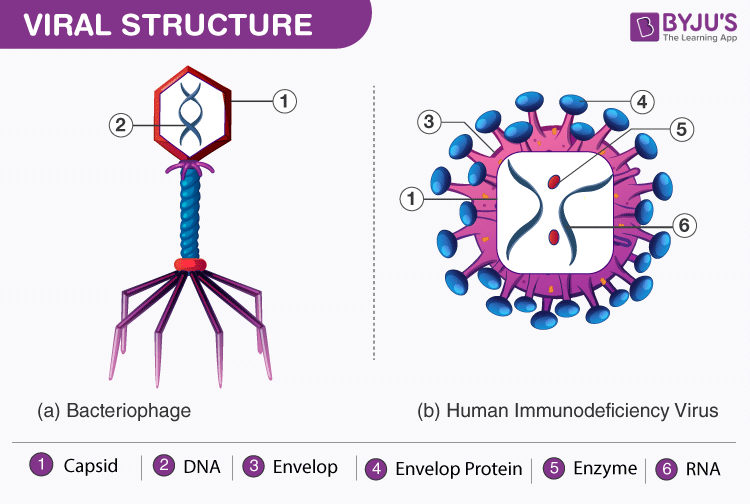
Wow, right?
So what is important to take away from that?
There is amazing, beautiful, tremendous diversity of life on this planet (not even looking at the extinct species).
Also, it is important to know the major kingdoms and what makes a mammal a mammal.
