The effects of plate tectonics:
Moving plates of Earth's crust cause massive alterations to the landscape. The three biggest effects of plate tectonics are:
Volcanoes
Earthquakes
Mountain formation
This unit will look at each of these in more depth.
Let's start with volcanoes:
There are two types of volcanoes because there are two types of magma:
The two types of magma are Mafic and Felsic
Mafic Felsic
From the core From melted seafloor
Hotter (1200 C) Cooler (600 C)
Thinner Thicker
Darker Lighter
Flows (friendly) Explodes (dangerous)
Shield volcano Stratovolcano
Found at divergent boundaries and hot spots Found at subduction zoens of convergent boundaries
Made of heavy metals Made of sand and shells





Now, let's look more closely at Mafic...
Mafic:
The magma is molten core and oozes up from Earth's interior until it breaks through the surface and erupts.
This molten core is composed of mostly heavy metals and is loosely bonded.

This hot molten rock is loosely bonded so the gases escape and the lava flows. It looks like this:
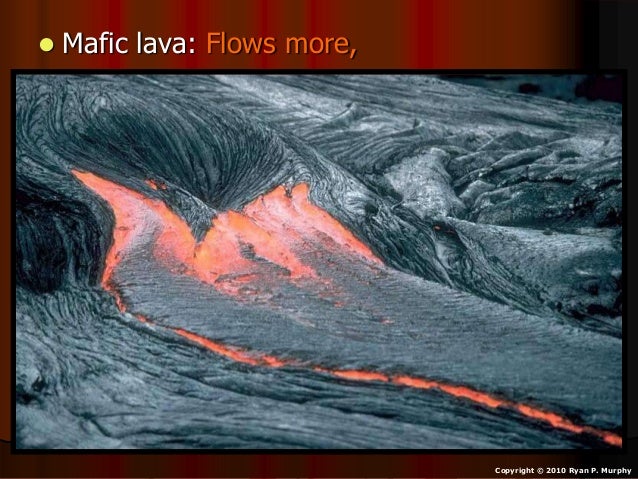



That flowing makes a gentlly shaped volcano called a "shield volcano" that looks like this:

You will notice that this type of magma is hot, dark, thin, and friendly. They are found where molten core breaks through the surface (divergent boundaries and hot spots).
Hot spots:

Now let's look closer at felsic...
Flesic:
Felsic is melted sea floor which is found at subduction zones of some convergent boundaries. It is light colored, cooler (600 C), but much thicker which means the gases bring the lava with them when they explode out (think shaken soda can).





When this ash settles back down, the volcano forms a classic shape called a "stratovolcao":

Sometimes the magma doesn't erupt. When that happens, the molten plume gets called an "igneous intrusion." They are worth looking at more closely:

Dikes, Sills, Laccoliths, and Batholiths are important.
Earthquakes:

Simply put all an earthquake is is anything that shakes the earth. There are millions of earthquakes each year resulting from the crustal plates sliding past one another.

Note the Focus and the Epicenter
The focus is the center of slippage. The epicenter is the place located above it where the earthquake is most felt.
The energy released travels in the form of waves:

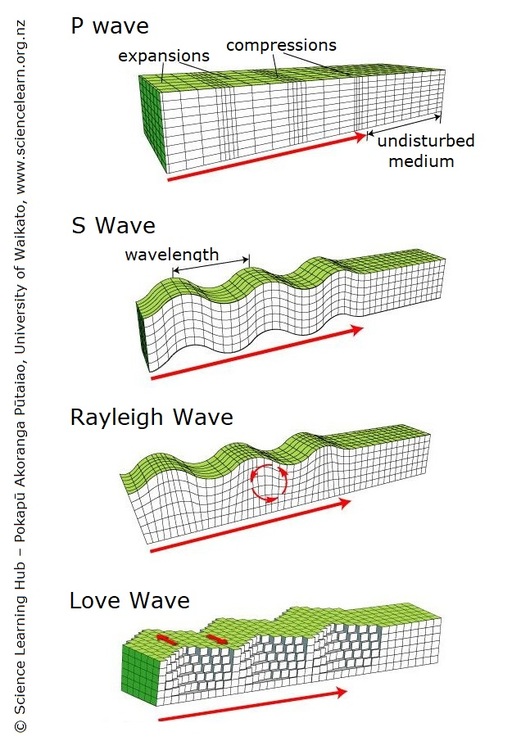
P-waves are the fastest and go through anything. They are compressional (like sound).
S-waves are second to arrive and go through only solids. They are transverse (like light).
Surface waves are last to arrive (if at all). They only travel a short distance and only at the surface of the Earth. They do all the damage. They are Love or Rayleigh waves.
We can measure these waves with seismograms:
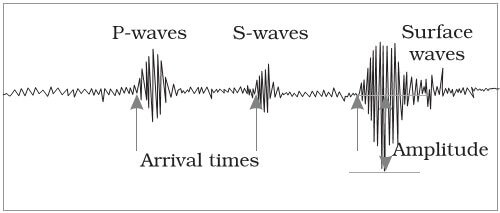
You need three of these readouts for each of the three dimensions and three stations to triangulate where the earthquake was.
But some places don't feel the earthquake.
Any guesses why?

Notice the Surface waves only travel a short distance and the S waves cannot travel through the core.
The S-waves do not go through liquids and so die at the outer core. This tells us that the core is liquid.
The P-waves get bent at the cores and, as you can see, have an band around Earth that they do not reach.
There is a lot of energy released when the Earth shakes:

It is measured:

Notice that slope. What that means is that each number is 10x as strong as the previous number!
Earthquakes are very damaging for many reasons. They may occur anywhere and at any time, they knock buildings over, they sever water and gas lines creating fires and preventing putting them out, they crumble roads and bridges making getting to help a challenge, they can knock down dams causing flooding and cutting back on water sources even more, they can break sewage lines contaminating water; they shake your very soul increasing depression.
The third effect of tectonic movements is mountain formation...
There are three processes that create mountains. They are convergent collisions of continents, volcano production, and dome mountains.
Continent collision:

We have learned about this already, but the two chunks of continent thrust upward (and downward) making the crumpled mountains (i.e. Himalayas)
Volcanoes:

We have learned about these already as well. Whether the melted rock is coming from the core (mafic) and forms a rounded shield mountain or whether it is melted seafloor at a subduction zone (felsic) and forms a pointy stratovolcano with steep sides, the mountain is made from this lava.
Dome mountain:

Yes, that is a laccolith that bulges the land above it. It produces a mountain or mountain "range" that is dome shaped:

You will notice that this is when the magma does not poke through and creates a dome like mountain or even a mountain "range."
Quick review:
Contrast Mafic and Felsic
How hot?
Where found?
Color?
Volcano shape?
Viscosity?
Danger level?
Define the igneous intrusions
Describe the three types of earthquake waves
What are the three mountain making processes