Reproduction:
Simple organisms can reproduce by simply growing and splitting much the way we grow.
This type of reproduction is "asexual" meaning that it is done with no regard to the sex of the organism and no exchange of genetic material.
That means that ALL OFFSPRING ARE GENETICALLY IDENTICAL TO THE PARENT!
The major advantage is that a partner is not necessary. The major disadvantage is that there is no variety in the population.
Examples of asexual reproduction include:
binary fission
budding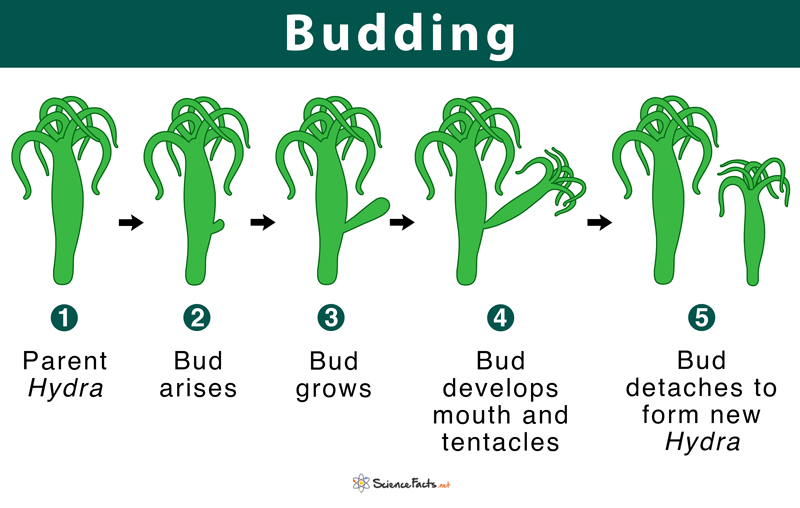
cuttings
runners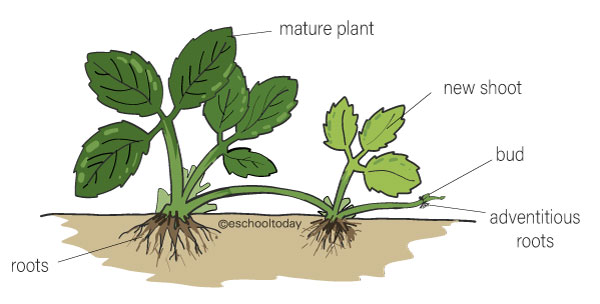
tubers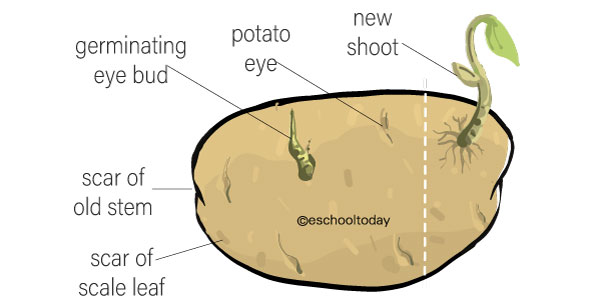
bulbs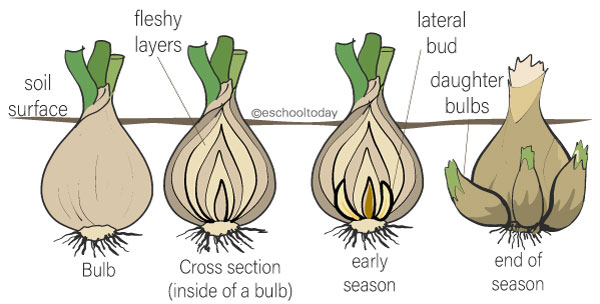
regeneration
etc.
What all of these asexual reproduction methods have in common is "Mitosis"
Mitosis is the process of reproducing a cell:

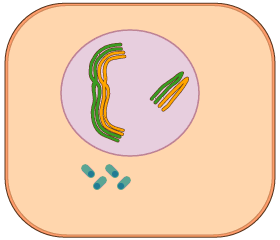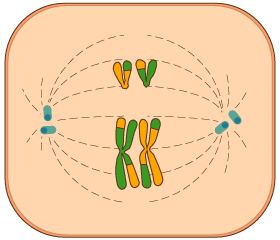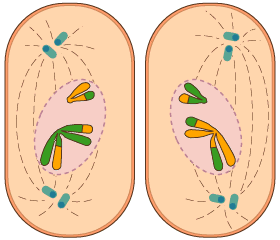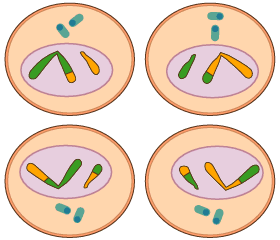
Interphase - resting followed by DNA duplication, but not much to see
Prophase - binding of the DNA around histones:

Metaphase - the bound DNA (chromotids) line up in the middle of the cell:

Anaphase - the DNA gets pulled apart by the centromeres

Telophase - the new nuclei form

Cytokinesis - the cell splits in two:

Here is Harper's drawing of it:
Sexual reproduction means that there are distinct sexes that divide their genetic material in half and then combine two halves to create a genetically different offspring.
This produces greater variety and therefore complexity. So most complex organisms reproduce sexually.
The splitting of DNA is similar to mitosis. It is called Meiosis and produces either one large ovum or four tiny sperm.
It goes through IPMAT followed by PMAT. During the first metaphase, the chromotids don't split, but instead half go one way and half goes the other. Without a second interphase, the DNA isn't doubled again. So during the second anaphase, the half DNA gets split. The result is four cells with half the DNA each.
Add a tail and an acrosome and you have made sperm (spermatogenesis). Oogenesis is similar, but all the cell contents get compiled into one of the four daughter cells and the other three die off as polar bodies.


Some organisms are hermaphrodites meaning that they have both male and female reproductive organs.
A good example of sexual reproduction is flowers. Prepare to dissect flowers!
Pistil Stamen
Stigma Filament
Style Anther
Ovary

A closer look at human development is important:
Once the sperm and egg meet, we call that conception and the resulting single cell a zygote. That zygote drifts down the fallopian tubes and implants in the uterus. There it will divide and part of it will develop into a placenta and send a message to the mother not to menstrate. The embryo (as it is called now that it has grown) begins to differentiate. This means that cells get cued to turn some of their DNA on and other DNA off. Once a cell differentiates, it can no longer develop into any type of cell. The cells are called stem cells before this differentiation and have obvious health benefits. After 8 weeks, the developing organism is called a fetus. Around 24 weeks, the human could (with help) survive. Around 40 weeks (give or take two weeks), the fetus sends a message to the mother that it is ready to be born and initiates the birth process.
Ectopic pregnancy
C-section
Twins - fraternal vs identical
What do all developing fetuses need?
Protection, nutrients (food and air), excretion of wastes, warmth, etc.
